What is CBD
Plants had served humans long before modern medicine was invented and continue to be natural solutions to fix ailments at home. CBD, the non-intoxicating molecule called a cannabinoid from the cannabis sativa plant, has surged in popularity in recent years. Since 2016, CBD sales in Switzerland with 1% THC – it's intoxicating equivalent – or less have skyrocketed. Most people use it as an alternative to self-treat medical conditions like insomnia, inflammation, pain, and anxiety. Since research on humans is still growing, CBD remains un-approved as a medical treatment and the healthcare perspective does not recommend self-treating. However, with the vast amount of anecdotal evidence, it is unlikely that people will stop trying. To make the best decision for your wellbeing, it is essential to understand how CBD works in your body and what you can expect from it.
The Endocannabinoid System
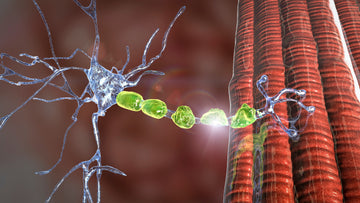
CBD, or cannabidiol, reacts with a unique system called the Endocannabinoid System or the ECS. The ECS is present in all mammals and plays a central role in maintaining equilibrium. It acts as a circuit board that connects the brain and many significant systems like the Endocrine, Immune, Central Nervous System, and Peripheral Nervous System. The ECS analyzes their information and gages what there needs to be more or less. It is not in charge of our functions, but rather how we perceive them. For example, the Endocrine System is responsible for regulating hormones that, amongst other things, influence our mood, metabolism, and development. But sometimes, especially during puberty, hormonal imbalances can cause a bad mood. This imbalance is where the ECS comes in. By sensing the dysfunction, it reestablishes healthy hormonal levels. The same applies to the Immune System and inflammation. While helpful in preventing infection and illness, too much inflammation can cause pain. The ECS can sense this and tell the Immune System to stop. But how exactly does this work? Interestingly enough, cannabinoids seem to be the key. It was only because of cannabis that scientists even discovered the ECS. Researchers suspected that cannabis reacted with a specific receptor in the brain, just like how opioids react with the opioid receptor. In 1988, the discovery of the CB receptors confirmed the hypothesis.
CB Receptors
The ECS can read all the other systems through its two primary cannabinoid receptors, CB1, and CB2. CB1 receptors are located in the brain, including but not limited to the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. These are involved with subconscious functions like breathing, memory, hunger, anger, and fear. CB2 receptors exist within the Central Nervous System, Peripheral Nervous System, Immune System, and white blood cells. Communication is the most critical part of any healthy entity, and the ECS is no exception. CB receptors communicate by releasing transmitters called endocannabinoids that send negative feedback loops to each. This constant exchange of information is how the ECS maintains balance throughout the body.
Endocannabinoids and Phyto-cannabinoids
There are two types of cannabinoids. The first is endogenous orendocannabinoids, meaning 'inside,' and they are what the body naturally produces. The two most prevalent ones are anandamide and 2-archidonyl glycerol, or 2-AG. Anandamide, or the 'bliss molecule,' helps control pain and has a strong affinity to the CB1 receptors. Affinity measures how tightly molecules bind to a receptor without activating it. 2-AG, while structurally similar to anandamide, is a full agonist, meaning it bonds and produces an effect to the CB1 receptor. The second type is called exogenous, or 'outside' cannabinoids. These come from cannabis or hemp and are usually called phytocannabinoids since phyto means 'plant'. The ECS, however, reads them and treats them as endocannabinoids. Whenever you take CBD, you stimulate the Endocannabinoid System. This action can be incredibly useful as even the ECS – the master regulator – can fall out of balance. When this happens, other conditions can arise or worsen. Therefore, taking CBD for anxiety, insomnia, or pain targets the root of the problem by restoring homeostasis.
Symptoms and Effects
Since CBD is non-intoxicating, meaning it won't produce a ‘high’ like how THC will, the effects are not so much felt, but rather seen. Common symptoms include decreased feelings of anxiety, sleeplessness, pain, or inflammation. Some people, however, describe it as a warm, calm ambiance washing over them. Different types of CBD products also produce slightly different effects. Smoking it from vapor, flower, or pollen, won't last as long as oils or edibles but will deliver an instant feeling. CBD comes as full-spectrum or isolate products. Isolates are CBD and nothing else, while full-spectrum contains all of the cannabinoids. From a holistic approach, full-spectrum is more effective. When all the plant components are left together, they work to create an overall better result. Pollen is an excellent full-spectrum option, as it retains all the cannabinoids, flavonoids, and terpenes from the flowers and leaves. Regardless of how you take it, CBD is non-addictive, synthesized and broken down quickly, with little to no side effects. Reported side effects have included dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, and irritability. The most alarming aspect of CBD is its tendency to interfere with pharmaceutical prescriptions the same way grapefruits do. If you are on any medications, make sure to check with your doctor before trying CBD.
What Can CBD Do for You?
It's important to acknowledge that CBD is a solution, not an antidote. There is more research to be done before we can fully understand CBD's intricate inner workings. Until then, none of its effects are guaranteed. However, given the versatility of the Endocannabinoid System and CBD's effects on it, it has become appealing to many people for a diverse set of reasons. If you are using CBD or considering using it, the most important thing you can do is educate yourself on how it works. Examine your life to see where you have imbalances. As we learn how integral the ECS is to our overall wellbeing, we see that many of our issues are a result of its dysfunction. Having a healthy Endocannabinoid System might prove to be how we heal the other parts of ourselves.